The primary aim of the risk management and business continuity policy is to ensure that there is a framework generally agreed upon by all stakeholders to address, reduce, or control potential risks. Hence, the university's need arose to adopt a clear policy for managing the risks it may face, whether administrative, financial, or otherwise.
The risk management policy is part of the university’s internal control functions and governance arrangements. Risk is defined as any event that could hinder the university’s ability to achieve its goals, and it is a link between the probability of an event occurring and the consequences of its occurrence.
- Ensuring the achievement of the university's strategic goals by knowing the expected risks and how to manage them.
- Unifying the methodology for predicting, studying, identifying, measuring, and determining the potential impacts of risks on the university’s goals, projects, investments, and assets, and planning how to respond to and control them.
- The policy explains the definition of risk, risk management, and the purpose of risk management.
- The policy explains the university's specific approach to risk management and documents the roles and responsibilities of relevant parties.
- The risk management policy is considered part of the university's oversight functions and governance arrangements.
- The policy describes the role of the risk management procedure in the entire control system and identifies the key reporting procedures, and explains the procedure that will be taken in order to assess the effectiveness of the control procedures.
- This policy should be reviewed once a year unless management deems a prior review necessary to ensure the continuity of the current policy.
- Changes to this policy must be made exclusively by management.
- Approved by management, the change log must remain up-to-date and be updated as soon as any change is made.
- Identify, assess, manage, monitor, review, report and deal with risks effectively.
- Applying the risk management system and its processes to the work systems implemented at the university, business continuity, effective governance and the integrated administrative system.
- Predicting potential risks, estimating their likelihood, severity, and level of danger, and implementing treatment plans while providing the necessary resources.
- Periodic review of risk management and its acceptance levels, and making informed decisions to reduce, eliminate, share, or bear it.
- Review the risk management policy and context annually to ensure consistency with the goals and expectations of senior management and stakeholders.
- Defining authorities and responsibilities towards risk management.
- Strengthening the culture of risk management at the university and raising employee awareness of its importance and everyone's responsibility for it.
- Continuous improvement in the risk management and reporting system.
- Identifying the range of risks facing the university.
- Classifying the group of risks facing the university.
- Continuously dealing with these risks and trying to reduce them.
- Regular meetings were held between the risk and business continuity manager and assistants to discuss cases and try to resolve and reduce them.
- Submitting periodic reports to the university agency to participate in reducing these risks.
The risk assessment methodology includes factors that prevent or hinder the entity implementing the guide from achieving its short, medium and long-term objectives, and the process may include the following:
- Risk identification is the process of identifying current or emerging risks in order to conduct a risk analysis.
- Risk analysis is the process of measuring potential risks based on the probability and impact of the risk before taking into account the existing controls in the entity.
- Risk assessment is the process of measuring the remaining risks after taking into account the entity's existing controls.
- Risk mitigation is the process of reducing the severity of the remaining risks to be addressed.
The Programs and Projects Unit archives, stores, monitors, updates, and continuously tracks the risk documents related to the strategic plan until the strategic plan is completed. Then, they are archived, stored, and recorded in the lessons learned. Each unit in the university stores risk documents and records related to its plans and projects in a way that makes them easy to refer to and benefit from in the future.
The Saudi Electronic University acknowledges that protecting its assets, operations, and services is a major responsibility in safeguarding the interests of its stakeholders. As part of the national initiative to automate and provide access services to its students, faculty, and staff, the university seeks to develop a viable plan for the continuity and recovery of its electronic services in the event of disasters.
The Saudi Electronic University is committed to continuing its efforts to monitor and restore operations at alternative facilities in the event of a sudden business interruption. The university and its senior management are also committed to developing and maintaining a viable business continuity plan that adheres to ethical insurance practices and aligns with the provisions and guidelines of the university's strategic and tactical plans. This plan will further support the university's philosophy of maintaining the highest quality of services for its students, faculty, and staff.
- The purpose of this policy is to define the objective, scope, and basic rules for business continuity management. This policy applies to the entire business continuity management system.
- The users of this document are all employees of the Saudi Electronic University, as well as all suppliers and external contracting staff who have a role in the business continuity management system.
The Saudi Electronic University plays a fundamental role in providing stakeholders, university employees, internal deanships, and departments with best-in-class Information Technology services and specialized solutions, while efficiently managing the available resources.
In this capacity, the University is fully committed to delivering continuous services to its customers and to protecting the interests of stakeholders in a manner that collectively ensures its ability to develop and grow. It is also committed to complying with all applicable legal and regulatory obligations, statutory requirements, and directives issued by relevant official governmental authorities.
The Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) is applied to all units, functions, processes, or business elements that are considered critical, and such entities must have recovery plans for their operations as part of an agreed strategy.
As an integral part of operational activities, the University adopts the following proactive and effective approaches to reduce the impact of any major incidents:
-
Establishing and maintaining a risk assessment and business impact analysis program, and a business continuity alignment program.
-
Developing business recovery plans and strategies to mitigate major risks.
-
Making business continuity and disaster recovery planning an essential part of the specifications for all current and new business requirements.
-
Providing policy requirements that obligate external service providers to have appropriate and tested recovery and emergency strategies.
-
Developing critical business applications to utilize system architectures that ensure continuous operation in the event of primary system failure.
-
Preparing testing and review plans, and conducting drills that build individuals’ confidence and awareness of their roles and the processes required to achieve objectives.
-
Continuously improving the suitability, efficiency, and effectiveness of the Business Continuity Management System.
This policy is based on the “Business Continuity Management – Requirements and Guidelines” standard issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO 22301 – Societal Security – Business Continuity Management Systems – Requirements).
This policy is communicated to all employees of the Saudi Electronic University. All members of the University community must respond to and comply with this policy as applicable. Each administration/sector/department is responsible for its readiness to manage business continuity at all times.
This policy is reviewed periodically to ensure its continued suitability, on an annual basis, as well as when significant changes occur.
- ISO 22301 standard requirements, including clauses 4.1, 4.3, 5.3, 6.2, and 9.1.1.
- Project plan for implementing the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS).
- List of legal, regulatory, contractual, and other applicable requirements.
- Risk treatment plan.
- Business continuity preparedness plan.
- Implementation of corrective and preventive actions.
- List of all contracts that obligate the organization to implement Business Continuity Management.
Accountability, transparency, respect for and commitment to laws, regulations, and ethical conduct are an integral part of the Saudi Electronic University in its various work and operations to achieve its goals, as the university seeks to adhere to all laws, instructions, and regulations on an ongoing basis.
The Compliance Policy defines the principles and standards for compliance and how to manage and mitigate the risks of non-compliance. Its objective is to ensure that non-compliance risks are adequately identified and mitigated, taking into account the nature, scope, and complexity of the business. In line with the university's strategy and vision, this policy aims to establish guidelines and standards to maintain the university's reputation and avoid any penalties that may arise from non-compliance.
The compliance policy applies to all departments and branches of the university.
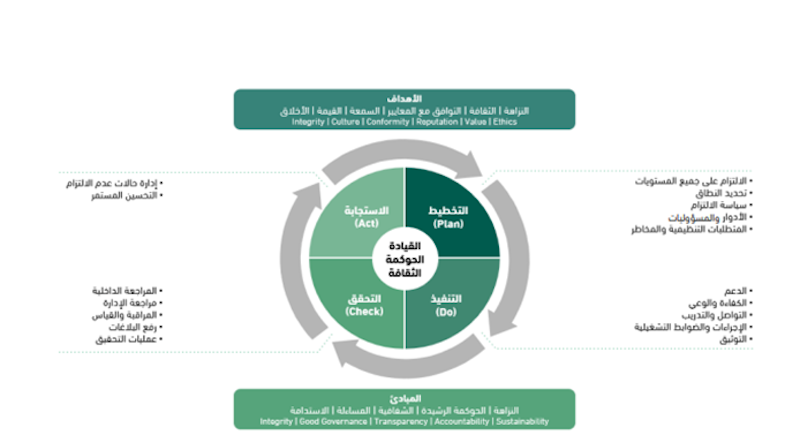
One of the main objectives of compliance is to ensure that the entity manages and implements its activities and operations in accordance with the regulations, rules, and other regulatory requirements that apply to it. However, there are other objectives that the compliance department seeks to achieve, which are as follows:
- Reducing the risk of non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Raising the level of compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Raising the level of maturity of compliance management practices at the university.
- Contributing to raising awareness and knowledge of the culture of commitment.
- Increasing awareness and commitment of university staff to the code of professional conduct.
- Effectively manage incoming reports related to cases of non-compliance.
- Providing support and advice to the various departments within the university in order to meet compliance requirements.
- Supporting and enabling the university to achieve its goals at all levels.
- Raising the level of commitment culture, practices and processes at the university level by using various means in a continuous and effective manner.
- Increasing stakeholder confidence in the university's work and activities by demonstrating that the university has a compliance program that contributes to effectively addressing and managing the risks of non-compliance.
- Enhancing the university's ability to proactively identify cases of non-compliance and take the necessary documentary and corrective actions to address them.
- Protecting and enhancing the reputation and standing of the university by mitigating the risks resulting from non-compliance with regulatory requirements and contributing to the prevention or detection of any behavior that is not in line with the code of conduct and ethics of public service and addressing it optimally.
These are the risks of legal or regulatory penalties, financial losses, or reputational damage that the university may suffer as a result of its non-compliance with relevant laws, regulations, rules, policies, internal work procedures, and external regulatory and supervisory legislation. The main risks of non-compliance are identified as follows:
Legal and regulatory risks: These refer to the risks of non-compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and professional practices, resulting in the following:
- Contract risks: The risks associated with the misinterpretation or non-application of legal rules relevant to a contract or transaction.
- Legislative risks: risks associated with changes in law and regulations.
- Sanction risks: These refer to the risk of judicial, administrative, or disciplinary sanctions being imposed as a result of non-compliance with laws, regulations, rules, standards, and/or contractual agreements.
- Reputational risks refer to the risks arising from a negative public opinion of the university due to declining university performance, genuine or false negative publicity, failures in academic practices, and failure to comply with current laws and regulations. Reputational risks can be more costly than financial losses.
The Saudi Electronic University's commitment is based on the following principles:
- Maintaining a good reputation and integrity is paramount.
The Saudi Electronic University enjoys a distinguished reputation among its clients and other universities. Maintaining this positive reputation requires the university and its staff to adhere to a policy of compliance. This can only be achieved through a thorough understanding and proper application of the laws and regulations of the regulatory bodies under which the Saudi Electronic University operates. - Senior management
supports the compliance department and ensures it has all the necessary authority and capabilities to fulfill its responsibilities independently. Management is responsible for adequate staffing and resources for the compliance department to implement this policy and for ensuring that these resources are effective and appropriate for managing non-compliance risks effectively. - Senior management
should set a good example and take all appropriate measures to ensure that all employees perform their work ethically, in accordance with compliance with regulatory, supervisory, and legislative controls and instructions and with the basic principles of the university. - Commitment is the responsibility of every employee.
Commitment is the basic principle of the university's policy and is the responsibility of every employee. It is also considered one of the most important basic criteria for the university to perform its tasks. - Supporting commitment to work:
The Saudi Electronic University believes that good and sound work must be supported by a strong commitment
The responsibility for compliance extends to ensuring that all business units adhere to and implement university policies. The university's compliance function is an independent function that identifies, evaluates, advises, monitors, and reports on the risks of non-compliance, which include exposure to legal or administrative penalties, financial losses, or reputational damage resulting from failure to comply with laws, regulatory controls, or standards of proper professional conduct and practice.
The three lines of defense:
The commitment function is considered an integral part of the three lines of defense of the Saudi Electronic University.
- First line of defense:
Within the framework of the first line of defense, the executive management has the responsibility for directly assessing, monitoring, and mitigating risks. - Second line of defense:
The second line of defense consists of the activities covered by the Internal Control Department – Compliance Department and Risk Management Department. - The third line of defense:
This represents internal auditing and inspection, and this guarantee includes confirmation of the effectiveness of the first and second lines of defense.
- Independence:
The Compliance Department is independent and reports directly to the University President. To ensure its impartiality and objectivity, the Compliance Department must not be placed in a position where there is a potential conflict of interest between its compliance responsibilities and any other responsibilities. It monitors all departments with potential non-compliance risks, in collaboration with the Internal Audit and Legal departments. The Compliance Department is also granted the independence to report violations and non-compliance to senior management. This independence does not preclude the Compliance team from working closely with relevant departments and their staff (the first line of defense). On the contrary, the working relationship should be collaborative in proactively identifying non-compliance risks. - Defining roles and responsibilities:
The compliance officer has all the powers that enable him to obtain all the data and information necessary for the purpose of reporting to senior management in accordance with the organizational structure. - Training and Qualification:
Compliance staff must be qualified and trained with a sound understanding of compliance laws, rules, and standards, and their actual impact on university operations. The professional skills of compliance staff are enhanced through systematically organized education and training courses.
- All relevant applicable legislation and laws.
- University policies and internal work regulations.
- The regulatory controls issued by all regulatory bodies.
- Work system.
The compliance criteria consist of a set of controls that are measured through the commitment of the university and its employees, and are as follows:
- Standards for measuring and evaluating university compliance:
This is achieved by establishing internal university policies and procedures in accordance with the laws and regulations governing its operations, whether these are local laws and regulations issued by legislative or regulatory bodies, in addition to applying international standards. University compliance can also be assessed through internal audit reports. - Standards for evaluating and measuring employee commitment:
Employee commitment is evaluated through personal and professional performance, both of which are related to employees’ complete understanding and commitment to the university’s policies, regulations, and work procedures, as well as the rules, systems, and performance charter that defines the employee’s responsibilities.
Maintaining transparency, cooperating with the university's regulatory bodies, and fulfilling obligations is critical to complying with regulatory requirements and effectively managing the risks of non-compliance in order to ensure that complete and accurate information is provided to all regulatory bodies.
If a regulatory body contacts a university administration regarding matters related to regulatory affairs and instructions, the Compliance Department must be notified immediately.
All departments responsible for preparing and submitting reports to regulatory, supervisory, or legislative bodies must ensure their reports include at least the following:
- Ensure that the submitted reports contain accurate and complete data, and that they are sent on time.
- A copy of all previous reports should be kept and sent to the Compliance Department, along with any attached documents.
- There should be work procedures within each department to regulate the process of preparing audit reports.
- Failure to submit the required reports on time or to comply with deadlines may subject the university to disciplinary penalties.